Guide To PCB Coating
PCB Coating is carried out to protect the Printed Circuit Board (PCB) from various environmental factors such as moisture, dust, chemicals, and temperature extremes. It also provides insulation and enhances the overall durability of the PCB. As such, it is an essential part of the manufacturing process.
Coating PCBs can increase their lifespan and reliability, reduce the risk of failure and enhance their resistance to corrosion and humidity. By making the PCBs more resistant to dust and debris, it can also help to maintain their performance over time.
In this guide we explore the different types of PCB coating there are.
Types of PCB Coating – Conformal
Conformal coating is polymeric film that is used to cover circuit boards, protecting them from a range of environmental and physical factors, helping to ensure component and product longevity.
It is a common choice of PCB protection as it offers good results and there are various conformal coating technologies available to meet different environmental requirements. Conformal coatings are generally thicker layers of protective material applied to the surface of the PCBs.
The popularity of this PCB coating has risen significantly in recent years, largely as a result of greater electronic miniaturisation and growth in wearable technology. The functionality of it is thought to be well suited to many types of circuit boards and products, including those with strict weight and thickness restrictions and where space is limited.
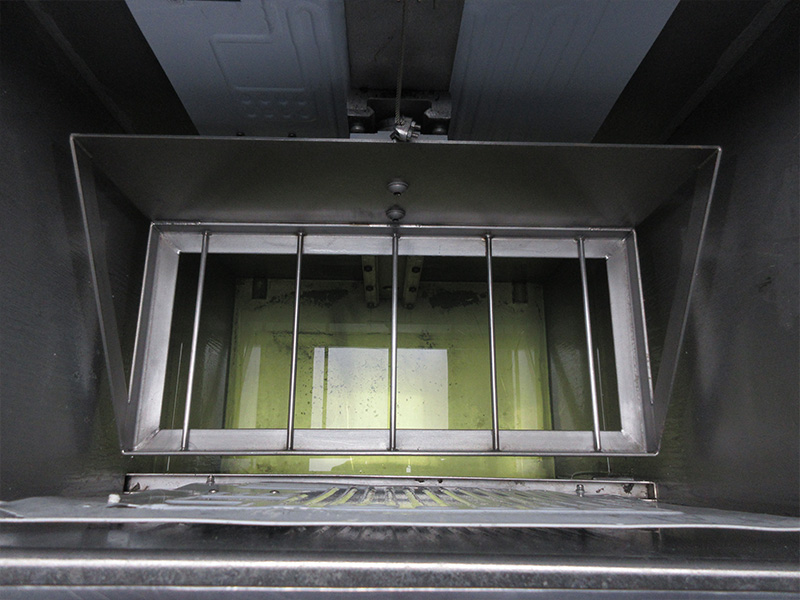

The most commonly used materials for conformal coating are acrylic, silicone, urethane, parylene and epoxy.
Acrylics are typically the most affordable option, while silicone coatings offer excellent flexibility and moisture resistance.
Urethane coatings are known for their chemical and abrasion resistance, and parylene coatings are a popular choice for medical and aerospace applications.
There are various methods for applying conformal coatings to PCBs, including spraying, brushing, dipping and selective coating.
Types of PCB Coating – Certonal
Certonal coating is a much thinner material and almost invisible to the eye.
There is only one type of Certonal coating available in the PCB industry, which is the proprietary Certonal material used to provide a complete barrier around electronic assemblies. Certonal is a fluorochemical polymer coating carried in a hydrofluoroether solvent.
Certonal Coating Application Methods
There are various methods for applying certonal coatings to PCBs, including spray, dip, brush, and vacuum deposition.
The spray method is used for large volume production, while dip and brush methods are used for small volume or touch-up applications. Vacuum deposition is used for high-performance applications that require a thin and uniform coating.
The choice of method depends on factors such as the PCB size, complexity, desired coating thickness, and production volume. Each method has its pros and cons, and electronic manufacturers must carefully consider these factors when selecting the most appropriate method for their application.
PCB Coating Standards and Certifications
Several standards and certifications are used to ensure that the PCB coatings meet industry requirements for quality and reliability.
Examples include UL 94, IPC-CC-830, and MIL-I-46058.
Certonal Or Conformal? Choosing The Right Coating
Choosing the right PCB coating depends on the specific requirements of the PCB and the environment in which it will be used. Factors to consider include the operating temperature range, exposure to moisture and chemicals, and the level of mechanical stress that the PCB will be subjected to. It is also worth considering the masking aspect, as conformal coatings are likely to need masking of certain components, for example connectors. Certonal coating does not require masking in most cases.
While both conformal and certonal coatings provide protection of electronic components that are prone to damage from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and other contaminants, Certonal coating offers several advantages over conformal coating, as follows:
Certonal coating uses a nanocomposite material to provide a complete barrier around electronic components, unlike conformal coating, which is a thin layer of material applied to the surface of the component.
Certonal coating provides superior protection against moisture and other contaminants, has high-temperature resistance and is highly resistant to abrasion, impact, and other forms of mechanical stress.
Certonal coating is resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents, making it ideal for use in harsh environments where electronic components are exposed to corrosive substances.
Conversely, conformal coatings have the following disadvantages:
It can still allow some moisture to penetrate through the coating, leading to corrosion and other forms of damage to electronic components.
Conformal coatings typically have lower temperature resistance and may break down at high temperatures, leaving the components vulnerable to damage.
They may not provide sufficient protection against chemical exposure, leading to damage to the components.
In conclusion, while conformal coating is still widely used in the electronics industry, certonal coating offers several advantages over conformal coating in terms of protection against moisture, high temperatures, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress.
Electronic manufacturers should consider Certonal coating as a more effective alternative to conformal coating for applications that require enhanced protection and durability.
Get in touch with a member of our team today to discuss your PCB coating requirements.
We’re here to help
If you’re looking for a PCB supplier, ready and prepared to adapt to your specific or changing needs, please contact us at

PCB Assembly
Precise, reliable PCB assembly to your exact requirements.
Box Build Assembly
Optimise your supply chain with our turnkey assembly service.
