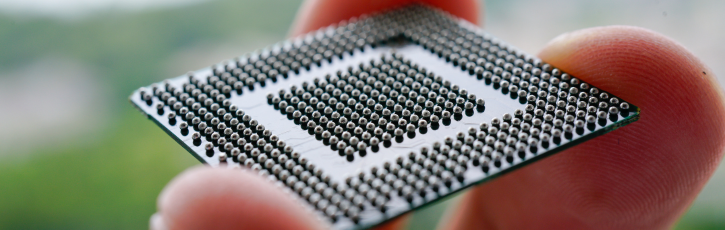
Ball Grid Arrays (BGAs) are transforming PCB assembly by enabling high-performance, compact designs for modern electronics. Whether you’re a product designer, engineer or purchasing professional, this blog explores the advantages, challenges and applications of BGAs, offering valuable insights for your next project.
What is a Ball Grid Array (BGA)?
A Ball Grid Array is a type of surface-mount packaging (i.e. a method of attaching components directly onto a Printed Circuit Board (PCB)’s surface). In particular, BGA is used to connect integrated circuits (ICs) to PCBs. It features a grid of tiny solder balls on its underside, which act as connectors. This design offers high-density interconnection, making it ideal for modern electronics where space is limited. BGA packages provide enhanced thermal and electrical performance compared to traditional pin-based packages. They are widely used in applications such as microprocessors, graphic cards and other high-performance devices due to their compact size and reliability.
Why BGAs are Essential in PCB Assembly
Ball Grid Arrays are crucial in PCB assembly due to their compact design, enabling high-density connections in limited spaces. They improve electrical and thermal performance by minimising resistance and enhancing heat dissipation. BGAs also support advanced miniaturisation, making them ideal for modern, high-performance electronics like smartphones and computers. Their solder ball grid ensures reliable, automated assembly, reducing production errors. As devices continue to demand smaller, more efficient solutions, BGAs remain indispensable in cutting-edge PCB technology.
Components and Construction of a Ball Grid Array
Ball Grid Arrays feature several key components and use advanced assembly techniques to ensure performance and reliability.
Ball Placement and Soldering Techniques
The distinctive feature of a BGA is its ‘array’ of solder balls on the underside, which replace traditional pins, to connect the different components to the PCB. The solder balls are evenly spaced, minimising the risk of accidental bridging.
These balls are precisely placed in a grid pattern to create electrical and mechanical connections. During PCB assembly, the solder balls melt using a reflow soldering process, forming strong and reliable bonds. The placement and uniformity of the solder balls are critical to ensuring consistent electrical performance.
Materials Used in BGAs
Ball Grid Arrays are constructed using a combination of materials. The substrate is typically made from organic laminate, supporting the silicon die (a semiconductor slice housing an integrated circuit) and providing pathways for electrical signals. The solder balls are composed of tin-lead or lead-free alloys, depending on environmental regulations. Encapsulation materials protect the chip from physical damage and contamination.
This combination of precise construction and high-quality materials makes BGAs a robust choice for modern electronics.
Types of Ball Grid Arrays
Ball Grid Arrays come in various types, each designed to meet specific performance, size and application requirements. Below are the most common types of BGAs and their unique characteristics:
Tape Ball Grid Array (TBGA)
TBGAs use a thin tape substrate to support the die and solder balls. They are lightweight and often used in applications requiring flexibility and heat dissipation, such as compact electronic devices.
Enhanced Ball Grid Array (EBGA)
EBGAs combine organic and ceramic materials to optimise thermal performance, electrical reliability and mechanical stability, making them ideal for high-performance applications like processors and graphics cards.
Metal Ball Grid Array (MBGA)
MBGAs use a metal core substrate to enhance mechanical stability and heat dissipation. This makes them well-suited for environments with high thermal demands.
Plastic Ball Grid Array (PBGA)
PBGAs feature a plastic substrate, making them cost-effective and lightweight. They are commonly used in consumer electronics, as well as automotive and telecommunications due to their affordability and performance.
Ceramic Ball Grid Array (CBGA)
CBGAs use a ceramic substrate, offering excellent thermal and mechanical stability. They are ideal for military, medical and aerospace applications where reliability and durability are critical.
Advantages of Using Ball Grid Arrays in PCB Assembly
Ball Grid Arrays offer several key advantages in PCB assembly, making them a popular choice for modern electronic devices.
Improved Electrical Performance
BGAs provide superior electrical performance due to their direct, low-resistance connections between the IC and PCB. The uniform placement of solder balls ensures efficient signal transmission and reduces the risk of electrical noise, enhancing overall circuit functionality.
Enhanced Thermal Management
The design of BGAs promotes efficient heat dissipation. The multiple solder balls offer better thermal conductivity, spreading heat more evenly across the component. This helps to prevent overheating, ensuring the reliability and longevity of sensitive electronic components.
Space-Saving Design
BGAs are ideal for compact, high-performance applications. The ball grid arrangement allows for more connections in a smaller area compared to traditional pin-based packages. This space-saving design makes BGAs particularly suitable for devices where space is at a premium, such as smartphones, laptops and wearables.
“Ball Grid Arrays are essential for high-performance PCB assemblies. While the specialised assembly techniques – like precise solder paste application and x-ray inspection to detect hidden defects – can increase costs, they ensure a robust, long-lasting connection. At our facility, we use automated pick and place machines and advanced reflow soldering techniques to ensure accurate and reliable results. Despite the higher initial cost and assembly complexity, BGAs provide unparalleled performance and are well worth the investment for high-density, space-constrained applications.”
|
Challenges and Limitations of BGAs
While Ball Grid Arrays offer numerous advantages in PCB assembly, they also come with certain challenges and limitations that must be considered.
Inspection and Repair Difficulties
One of the primary challenges with BGAs is the difficulty in inspecting and repairing connections. Since the solder balls are placed beneath the package, traditional visual inspection methods cannot easily detect soldering issues. Specialised x-ray equipment is often required to check for defects such as solder bridges or misalignments, which adds complexity and cost to the assembly process. Repairing faulty BGAs can also be challenging, as it requires advanced rework tools and techniques.
Cost Considerations
BGAs tend to be more expensive than traditional packaging options due to their complex manufacturing processes and the need for advanced inspection equipment. Additionally, the specialised soldering and rework tools required for BGAs increase overall production costs. This can make BGAs less cost-effective for low-volume or budget-sensitive projects, particularly when alternative packaging methods could suffice.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of BGAs often outweigh the limitations, particularly for high-performance, compact electronic devices.

Applications of Ball Grid Arrays
Ball Grid Arrays are widely used in a variety of electronic applications due to their compact size, superior performance and reliability. Their versatility makes them ideal for numerous industries and devices.
Common Use Cases in Modern Electronics
BGAs are typically found in high-performance consumer electronics, including smartphones, laptops, gaming consoles and tablets. Their ability to handle high-density interconnections and provide efficient thermal management makes them suitable for processors, memory modules and Graphics Processing Units (GPUs).
Industry Examples Leveraging BGAs
In the consumer electronics sector, BGAs are integral to processors and chips in smartphones, helping improve performance while reducing device size. Automotive manufacturers use BGAs for critical components like engine control units (ECUs) and sensors, ensuring durability in harsh environments. The aerospace industry relies on BGAs for avionics systems, where high performance and reliability are essential. Moreover, medical devices such as pacemakers and diagnostic equipment also benefit from BGA technology due to their compact size and consistent performance.
BGAs are indispensable in modern electronics, offering high-performance capabilities in a wide range of industries.
How to Work with Ball Grid Arrays in PCB Assembly
Tips for Designing PCBs with BGAs
- Ensure Proper Pad Layout: Design the PCB with accurate pad spacing to align with the BGA ball grid, ensuring reliable connections
- Consider Trace Width: Make sure the traces leading to the BGA pads are appropriately sized to handle the electrical current without overheating
- Add Sufficient Via Connections: Use via-in-pad designs for high-density boards and ensure there is enough room for vias to avoid signal interference
- Account for Thermal Management: Include heat dissipation features such as thermal vias or dedicated copper planes to prevent overheating of BGA components
- Design for Easy Inspection: Incorporate visual inspection features, such as sufficient space around the BGA, to make it easier to detect soldering issues and avoid hidden defects.
Guidelines for Soldering and Assembly
- Use Precision Equipment: Ensure you use a high-quality reflow oven or soldering system to achieve even soldering of all BGA balls
- Preheat the PCB: Properly preheat the PCB to prevent thermal shock and ensure uniform soldering
- Apply Solder Paste Carefully: Use an appropriate amount of solder paste on each pad, avoiding excess that could cause bridging
- Inspect with X-Ray: After soldering, use x-ray inspection to check for hidden defects such as cold solder joints or bridging between the solder balls.
Following these tips and guidelines will help you work effectively with BGAs, ensuring a reliable and high-performance PCB assembly.
Conclusion: The Future of Ball Grid Arrays
As the demand for smaller, more powerful and energy-efficient electronics continues to grow, the role of Ball Grid Arrays will only become more significant. With advancements in manufacturing technologies, BGAs are expected to evolve, becoming even more compact and efficient in their design. Their ability to provide high-density interconnections and superior thermal management will be crucial for the next generation of devices, from wearables to automotive and medical technologies. Additionally, as industries focus on sustainability, improvements in BGA materials and processes may lead to greener, more environmentally friendly solutions. Ultimately, we see BGAs remaining at the heart of modern PCB assembly, meeting the challenges of miniaturisation and performance in the fast-evolving electronics landscape.
MPE Electronics is an established and experienced contract electronics manufacturer specialising in PCB assemblies and full box build assembly for a wide range of commercial and industrial businesses.
To find out how MPE Electronics’ PCB manufacturing and assembly services can benefit your business, contact our expert and friendly team on +44 (0)1825 764822 or enquiries@mpe-electronics.co.uk.